您现在的位置是:网站首页> 编程资料编程资料
SSH蜜罐:kippo的详细介绍_工具使用_网络安全_
![]() 2023-05-24
542人已围观
2023-05-24
542人已围观
简介 SSH蜜罐:kippo的详细介绍_工具使用_网络安全_
蜜网是指另外采用了技术的蜜罐,从而以合理方式记录下黑客的行动,同时尽量减小或排除对因特网上其它系统造成的风险。建立在反向防火墙后面的蜜罐就是一个例子。防火墙的目的不是防止入站连接,而是防止蜜罐建立出站连接。不过,虽然这种方法使蜜罐不会破坏其它系统,但同时很容易被黑客发现。
数据收集是设置蜜罐的另一项技术挑战。蜜罐监控者只要记录下进出系统的每个数据包,就能够对黑客的所作所为一清二楚。蜜罐本身上面的日志文件也是很好的数据来源。但日志文件很容易被攻击者删除,所以通常的办法就是让蜜罐向在同一网络上但防御机制较完善的远程系统日志服务器发送日志备份。(务必同时监控日志服务器。如果攻击者用新手法闯入了服务器,那么蜜罐无疑会证明其价值。)
蜜罐系统的优点之一就是它们大大减少了所要分析的数据。对于通常的网站或邮件服务器,攻击流量通常会被合法流量所淹没。而蜜罐进出的数据大部分是攻击流量。因而,浏览数据、查明攻击者的实际行为也就容易多了。
自1999年启动以来,蜜网计划已经收集到了大量信息。部分发现结果包括:攻击率在过去一年增加了一倍;攻击者越来越多地使用能够堵住漏洞的自动点击工具(如果发现新漏洞,工具很容易更新);尽管虚张声势,但很少有黑客采用新的攻击手法。
打开SERVER
安装
root@ubuntu:~# mkdir kippo
root@ubuntu:~# apt-get install python-dev openssl python-openssl python-pyasn1 python-twisted python-mysqldb
获得源代码
root@ubuntu:~# cd kippo/
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# svn checkout http://kippo.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/ .
添加一个独立的用户组给KIPPO
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# useradd -s /bin/bash -d /home/kippo -m kippo
添加一个独立的MYSQL用户给KIPPO
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 34
Server version: 5.1.61-0ubuntu0.10.10.1-log (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE kippo;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL ON kippo.* to 'kippo'@'localhost' identified by '123456';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| kippo |
| mysql |
| pentest |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql>
帐号和数据库一样 密码123456
导入默认数据库 #本文地址http://fuzzexp.org/ssh_honeypot_kippo.html
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# cd doc/sql/
root@ubuntu:~/kippo/doc/sql# ls
mysql.sql update2.sql update3.sql update4.sql update5.sql update6.sql
root@ubuntu:~/kippo/doc/sql# mysql -ukippo -p123456 kippo < mysql.sql
编辑配置
kippo.cfg.dist
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# mv kippo.cfg.dist kippo.cfg
编辑他 我的如下:
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# cat kippo.cfg
#
# Kippo configuration file (kippo.cfg)
#
[honeypot]
# IP addresses to listen for incoming SSH connections.
#
# (default: 0.0.0.0) = any address
ssh_addr = 0.0.0.0
# Port to listen for incoming SSH connections.
#
# (default: 2222)
ssh_port = 2222
# Hostname for the honeypot. Displayed by the shell prompt of the virtual
# environment.
#
# (default: sales)
hostname = ubuntu
# Directory where to save log files in.
#http://fuzzexp.org/?p=5571
# (default: log)
log_path = log
# Directory where to save downloaded (malware) files in.
#
# (default: dl)
download_path = dl
# Directory where virtual file contents are kept in.
#
# This is only used by commands like 'cat' to display the contents of files.
# Adding files here is not enough for them to appear in the honeypot - the
# actual virtual filesystem is kept in filesystem_file (see below)
#
# (default: honeyfs)
contents_path = honeyfs
# File in the python pickle format containing the virtual filesystem.
#
# This includes the filenames, paths, permissions for the whole filesystem,
# but not the file contents. This is created by the createfs.py utility from
# a real template linux installation.
#
# (default: fs.pickle)
filesystem_file = fs.pickle
# Directory for miscellaneous data files, such as the password database.
#
# (default: data_path)
data_path = data
# Directory for creating simple commands that only output text.
#
# The command must be placed under this directory with the proper path, such
# as:
# txtcmds/usr/bin/vi
# The contents of the file will be the output of the command when run inside
# the honeypot.
#
# In addition to this, the file must exist in the virtual
# filesystem {filesystem_file}
# (default: txtcmds)
txtcmds_path = txtcmds
# Public and private SSH key files. If these don't exist, they are created
# automatically.
#
# (defaults: public.key and private.key)
public_key = public.key
private_key = private.key
# Initial root password. NO LONGER USED!
# Instead, see {data_path}/userdb.txt
password = 123456
# IP address to bind to when opening outgoing connections. Used exclusively by
# the wget command.
#
# (default: not specified)
out_addr = 0.0.0.0
# Sensor name use to identify this honeypot instance. Used by the database
# logging modules such as mysql.
#
# If not specified, the logging modules will instead use the IP address of the
# connection as the sensor name.
#
# (default: not specified)
#sensor_name=myhostname
# Fake address displayed as the address of the incoming connection.
# This doesn't affect logging, and is only used by honeypot commands such as
# 'w' and 'last'
#
# If not specified, the actual IP address is displayed instead (default
# behaviour).
#
# (default: not specified)
#fake_addr = 192.168.66.254
# Banner file to be displayed before the first login attempt.
#
# (default: not specified)
#banner_file =
# Session management interface.
#
# This is a telnet based service that can be used to interact with active
# sessions. Disabled by default.
#
# (default: false)
interact_enabled = false
# (default: 5123)
interact_port = 5123
# MySQL logging module
#
# Database structure for this module is supplied in doc/sql/mysql.sql
#
# To enable this module, remove the comments below, including the
# [database_mysql] line.
[database_mysql]
host = localhost
database = kippo
username = kippo
password = 123456
# XMPP Logging
#
# Log to an xmpp server.
# For a detailed explanation on how this works, see:
#
# To enable this module, remove the comments below, including the
# [database_xmpp] line.
#[database_xmpp]
#server = sensors.carnivore.it
#user = anonymous@sensors.carnivore.it
#password = anonymous
#muc = dionaea.sensors.carnivore.it
#signal_createsession = kippo-events
#signal_connectionlost = kippo-events
#signal_loginfailed = kippo-events
#signal_loginsucceeded = kippo-events
#signal_command = kippo-events
#signal_clientversion = kippo-events
#debug=true
root@ubuntu:~/kippo#
安装监听工具
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# apt-get install authbind
配置
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# chown kippo:kippo /etc/authbind/byport/22
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# chmod 777 /etc/authbind/byport/22
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# chown -R kippo:kippo /root/kippo/
创建一个启动脚本
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# echo "twistd -y kippo.tac -l log/kippo.log --pidfile kippo.pid" > 1.sh
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# cat 1.sh
twistd -y kippo.tac -l log/kippo.log --pidfile kippo.pid
root@ubuntu:~/kippo#
移动工具位置
root@ubuntu:~# mv kippo/ /opt/
root@ubuntu:~# cd /opt/
root@ubuntu:/opt# ls
kippo
root@ubuntu:/opt# cd kippo/
更改下KIPPO用户密码 切换到KIPPO
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# passwd kippo
Enter new UNIX password:
Retype new UNIX password:
passwd: password updated successfully
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# su kippo
kippo@ubuntu:/root/kippo$ id
uid=1002(kippo) gid=1002(kippo) groups=1002(kippo)
kippo@ubuntu:/root/kippo$
启动

kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$ pwd
/opt/kippo
kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$ ./start.sh
Starting kippo in background...Loading dblog engine: mysql
Generating RSA keypair...
done.
查看监听
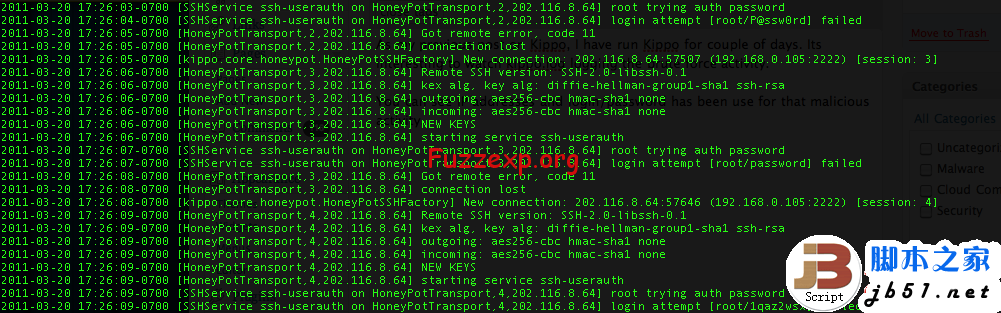
kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$ netstat -antp
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.)
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:587 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2222 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4615/python
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 192.168.71.130:22 192.168.71.129:44874 ESTABLISHED -
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN -
kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2222 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4615/python
查找进程
kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$ ps -ef | grep 4615
kippo 4615 1 0 13:47 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/twistd -y kippo.tac -l log/kippo.log --pidfile kippo.pid
kippo 4626 4588 0 13:48 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto 4615
kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$
扫描下UB kippo的配置文件端口定义为2222
root@Dis9Team:~# nmap -sV 192.168.71.130 -p 2222
Starting Nmap 5.51 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2012-10-11 22:51 PDT
Nmap scan report for 192.168.71.130
Host is up (0.00024s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
2222/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 5.1p1 Debian 5 (protocol 2.0)
MAC Address: 00:0C:29:9E:3F:14 (VMware)
Service Info: OS: Linux
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at http://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0
数据收集是设置蜜罐的另一项技术挑战。蜜罐监控者只要记录下进出系统的每个数据包,就能够对黑客的所作所为一清二楚。蜜罐本身上面的日志文件也是很好的数据来源。但日志文件很容易被攻击者删除,所以通常的办法就是让蜜罐向在同一网络上但防御机制较完善的远程系统日志服务器发送日志备份。(务必同时监控日志服务器。如果攻击者用新手法闯入了服务器,那么蜜罐无疑会证明其价值。)
蜜罐系统的优点之一就是它们大大减少了所要分析的数据。对于通常的网站或邮件服务器,攻击流量通常会被合法流量所淹没。而蜜罐进出的数据大部分是攻击流量。因而,浏览数据、查明攻击者的实际行为也就容易多了。
自1999年启动以来,蜜网计划已经收集到了大量信息。部分发现结果包括:攻击率在过去一年增加了一倍;攻击者越来越多地使用能够堵住漏洞的自动点击工具(如果发现新漏洞,工具很容易更新);尽管虚张声势,但很少有黑客采用新的攻击手法。
打开SERVER
安装
root@ubuntu:~# mkdir kippo
root@ubuntu:~# apt-get install python-dev openssl python-openssl python-pyasn1 python-twisted python-mysqldb
获得源代码
root@ubuntu:~# cd kippo/
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# svn checkout http://kippo.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/ .
添加一个独立的用户组给KIPPO
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# useradd -s /bin/bash -d /home/kippo -m kippo
添加一个独立的MYSQL用户给KIPPO
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 34
Server version: 5.1.61-0ubuntu0.10.10.1-log (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE kippo;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> GRANT ALL ON kippo.* to 'kippo'@'localhost' identified by '123456';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| kippo |
| mysql |
| pentest |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
mysql>
帐号和数据库一样 密码123456
导入默认数据库 #本文地址http://fuzzexp.org/ssh_honeypot_kippo.html
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# cd doc/sql/
root@ubuntu:~/kippo/doc/sql# ls
mysql.sql update2.sql update3.sql update4.sql update5.sql update6.sql
root@ubuntu:~/kippo/doc/sql# mysql -ukippo -p123456 kippo < mysql.sql
编辑配置
kippo.cfg.dist
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# mv kippo.cfg.dist kippo.cfg
编辑他 我的如下:
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# cat kippo.cfg
#
# Kippo configuration file (kippo.cfg)
#
[honeypot]
# IP addresses to listen for incoming SSH connections.
#
# (default: 0.0.0.0) = any address
ssh_addr = 0.0.0.0
# Port to listen for incoming SSH connections.
#
# (default: 2222)
ssh_port = 2222
# Hostname for the honeypot. Displayed by the shell prompt of the virtual
# environment.
#
# (default: sales)
hostname = ubuntu
# Directory where to save log files in.
#http://fuzzexp.org/?p=5571
# (default: log)
log_path = log
# Directory where to save downloaded (malware) files in.
#
# (default: dl)
download_path = dl
# Directory where virtual file contents are kept in.
#
# This is only used by commands like 'cat' to display the contents of files.
# Adding files here is not enough for them to appear in the honeypot - the
# actual virtual filesystem is kept in filesystem_file (see below)
#
# (default: honeyfs)
contents_path = honeyfs
# File in the python pickle format containing the virtual filesystem.
#
# This includes the filenames, paths, permissions for the whole filesystem,
# but not the file contents. This is created by the createfs.py utility from
# a real template linux installation.
#
# (default: fs.pickle)
filesystem_file = fs.pickle
# Directory for miscellaneous data files, such as the password database.
#
# (default: data_path)
data_path = data
# Directory for creating simple commands that only output text.
#
# The command must be placed under this directory with the proper path, such
# as:
# txtcmds/usr/bin/vi
# The contents of the file will be the output of the command when run inside
# the honeypot.
#
# In addition to this, the file must exist in the virtual
# filesystem {filesystem_file}
# (default: txtcmds)
txtcmds_path = txtcmds
# Public and private SSH key files. If these don't exist, they are created
# automatically.
#
# (defaults: public.key and private.key)
public_key = public.key
private_key = private.key
# Initial root password. NO LONGER USED!
# Instead, see {data_path}/userdb.txt
password = 123456
# IP address to bind to when opening outgoing connections. Used exclusively by
# the wget command.
#
# (default: not specified)
out_addr = 0.0.0.0
# Sensor name use to identify this honeypot instance. Used by the database
# logging modules such as mysql.
#
# If not specified, the logging modules will instead use the IP address of the
# connection as the sensor name.
#
# (default: not specified)
#sensor_name=myhostname
# Fake address displayed as the address of the incoming connection.
# This doesn't affect logging, and is only used by honeypot commands such as
# 'w' and 'last'
#
# If not specified, the actual IP address is displayed instead (default
# behaviour).
#
# (default: not specified)
#fake_addr = 192.168.66.254
# Banner file to be displayed before the first login attempt.
#
# (default: not specified)
#banner_file =
# Session management interface.
#
# This is a telnet based service that can be used to interact with active
# sessions. Disabled by default.
#
# (default: false)
interact_enabled = false
# (default: 5123)
interact_port = 5123
# MySQL logging module
#
# Database structure for this module is supplied in doc/sql/mysql.sql
#
# To enable this module, remove the comments below, including the
# [database_mysql] line.
[database_mysql]
host = localhost
database = kippo
username = kippo
password = 123456
# XMPP Logging
#
# Log to an xmpp server.
# For a detailed explanation on how this works, see:
#
# To enable this module, remove the comments below, including the
# [database_xmpp] line.
#[database_xmpp]
#server = sensors.carnivore.it
#user = anonymous@sensors.carnivore.it
#password = anonymous
#muc = dionaea.sensors.carnivore.it
#signal_createsession = kippo-events
#signal_connectionlost = kippo-events
#signal_loginfailed = kippo-events
#signal_loginsucceeded = kippo-events
#signal_command = kippo-events
#signal_clientversion = kippo-events
#debug=true
root@ubuntu:~/kippo#
安装监听工具
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# apt-get install authbind
配置
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# chown kippo:kippo /etc/authbind/byport/22
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# chmod 777 /etc/authbind/byport/22
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# chown -R kippo:kippo /root/kippo/
创建一个启动脚本
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# echo "twistd -y kippo.tac -l log/kippo.log --pidfile kippo.pid" > 1.sh
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# cat 1.sh
twistd -y kippo.tac -l log/kippo.log --pidfile kippo.pid
root@ubuntu:~/kippo#
移动工具位置
root@ubuntu:~# mv kippo/ /opt/
root@ubuntu:~# cd /opt/
root@ubuntu:/opt# ls
kippo
root@ubuntu:/opt# cd kippo/
更改下KIPPO用户密码 切换到KIPPO
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# passwd kippo
Enter new UNIX password:
Retype new UNIX password:
passwd: password updated successfully
root@ubuntu:~/kippo# su kippo
kippo@ubuntu:/root/kippo$ id
uid=1002(kippo) gid=1002(kippo) groups=1002(kippo)
kippo@ubuntu:/root/kippo$
启动

kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$ pwd
/opt/kippo
kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$ ./start.sh
Starting kippo in background...Loading dblog engine: mysql
Generating RSA keypair...
done.
查看监听

kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$ netstat -antp
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.)
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:587 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2222 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4615/python
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 192.168.71.130:22 192.168.71.129:44874 ESTABLISHED -
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN -
kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:2222 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4615/python
查找进程
kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$ ps -ef | grep 4615
kippo 4615 1 0 13:47 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/twistd -y kippo.tac -l log/kippo.log --pidfile kippo.pid
kippo 4626 4588 0 13:48 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto 4615
kippo@ubuntu:/opt/kippo$
扫描下UB kippo的配置文件端口定义为2222
root@Dis9Team:~# nmap -sV 192.168.71.130 -p 2222
Starting Nmap 5.51 ( http://nmap.org ) at 2012-10-11 22:51 PDT
Nmap scan report for 192.168.71.130
Host is up (0.00024s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
2222/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 5.1p1 Debian 5 (protocol 2.0)
MAC Address: 00:0C:29:9E:3F:14 (VMware)
Service Info: OS: Linux
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at http://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0
相关内容
- 自定义bash脚本定制自动化各种渗透测试任务_工具使用_网络安全_
- 在VPS上搭建远程桌面蜜罐的方法介绍_工具使用_网络安全_
- nmap常用命令及参数说明 _工具使用_网络安全_
- 关于杀毒软件安装使用的几个误区 杀毒软件也要慎用_工具使用_网络安全_
- 在线破解各类加密密码地址( 干掉收费cmd5)_工具使用_网络安全_
- 使用CA和CCA克隆账户与检查账号是否被克隆工具的方法_工具使用_网络安全_
- MT.EXE 中文使用教程_工具使用_网络安全_
- rar.exe 在提权中的妙用_工具使用_网络安全_
- 让自解压文件在右键中不显示的实现方法_工具使用_网络安全_
- reDuh 简单使用说明_工具使用_网络安全_





